Passive Optical Networks (PONs) have revolutionized fiber-optic communication, providing cost-effective and high-bandwidth solutions for residential and business users. Within a PON architecture, several key components play a crucial role, including the Optical Line Terminal (OLT), Optical Network Unit (ONU), Optical Network Terminal (ONT), and Optical Distribution Network (ODN). This article delves into the functions and significance of these components.
Optical Line Terminal (OLT)
The OLT serves as the central hub of a PON system. It connects to the core network and is responsible for managing and controlling the entire PON network. The OLT provides the interface between the optical fiber and the electrical signals, converting optical signals received from ONUs into electrical signals for further processing. Additionally, it generates optical signals and transmits them downstream to the ONUs. The OLT typically operates at the service provider's premises and is a highly reliable and powerful device capable of handling a large number of ONUs.
Optical Network Unit (ONU)
The ONU is the customer-side device in a PON system. It connects to the user's equipment, such as computers, routers, or set-top boxes, and provides the interface between the optical fiber and the user's network. The ONU converts the optical signals received from the OLT into electrical signals for use by the user's devices. Conversely, it converts electrical signals from the user's devices into optical signals and transmits them upstream to the OLT. ONUs are typically installed at the customer's premises and are designed to be reliable, compact, and easy to install.
Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
An ONT is similar to an ONU, but it offers additional functionality. An ONT typically provides multiple services, such as voice, data, and video, over a single fiber connection. It integrates multiple services onto a single device, simplifying installation and management for both the service provider and the customer. ONTs are commonly used in residential and small business applications where multiple services are required.
Optical Distribution Network (ODN)
The ODN is the passive optical network infrastructure that connects the OLT to the ONUs/ONTs. It consists of optical fibers, splitters, connectors, and other passive components that distribute the optical signals from the OLT to the ONUs/ONTs. The ODN is responsible for transporting the optical signals without any active electronic components, ensuring low loss and high reliability. The ODN is a crucial part of a PON system, as it enables the delivery of high-bandwidth services to multiple customers over a shared fiber infrastructure.
In conclusion, the OLT, ONU, ONT, and ODN are integral components of a PON system. The OLT serves as the central hub, managing and controlling the network, while the ONUs/ONTs provide the customer-side interface. The ODN connects the OLT to the ONUs/ONTs, transporting optical signals reliably over a shared fiber infrastructure. Together, these components enable PON systems to deliver high-bandwidth services cost-effectively to multiple customers.
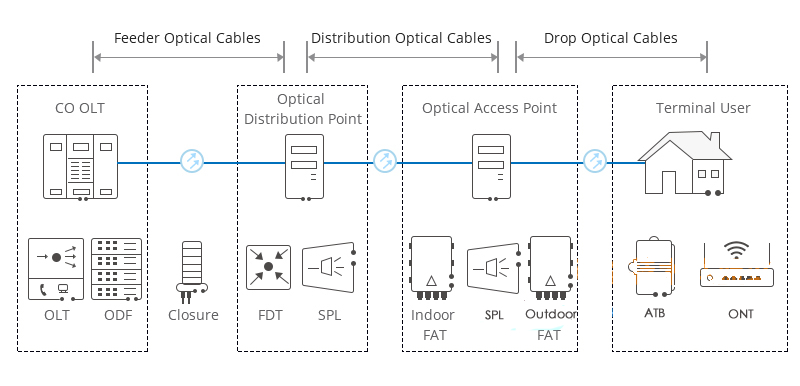
he diagram of the networking configuration for OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN is as follows


